American Alligator
| Class: Reptilia:
Reptiles |
Diet: Small mammals |
| Order:
Crocodilia: Crocodiles, Alligators, Gavial |
| Size: up
to 5.5 m (18 ft) |
| Family: Alligatorianae:
Alligators and Caimans |
Conservation Status: Non-threatened
|
| Scientific Name:
Alligator mississipiensis |
Habitat: marshes,
rivers, swamps |
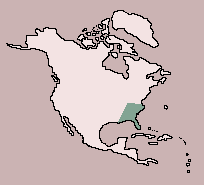
| Range:
Southeastern USA |
 The
American alligator, once struggling for survival against hunters and habitat
destruction, has been so effectively protected by conservation laws that
the population is now on the increase. These alligators usually mate in
shallow water in April, and courtship is slow and quiet. The male stays
with the female for several days before mating, occasionally stroking her
body with his forelimbs. As she nears acquiescence, he rubs her throat
with his head and blows bubbles past her cheeks. The female finds a nest
site near water and scrapes up whatever plant debris is available with
sweeping movements of her body and tail. She packs the vegetation together
to form a mound, with a cavity for the eggs. She lays 28 to 52 eggs and
crawls over the mound to close the cavity with more vegetation. She guards
the nest while the eggs incubate for about 65 days. The hatching young
call out to their mother, prompting her to open the nest and free them.
They remain with her for up to 3 years. The
American alligator, once struggling for survival against hunters and habitat
destruction, has been so effectively protected by conservation laws that
the population is now on the increase. These alligators usually mate in
shallow water in April, and courtship is slow and quiet. The male stays
with the female for several days before mating, occasionally stroking her
body with his forelimbs. As she nears acquiescence, he rubs her throat
with his head and blows bubbles past her cheeks. The female finds a nest
site near water and scrapes up whatever plant debris is available with
sweeping movements of her body and tail. She packs the vegetation together
to form a mound, with a cavity for the eggs. She lays 28 to 52 eggs and
crawls over the mound to close the cavity with more vegetation. She guards
the nest while the eggs incubate for about 65 days. The hatching young
call out to their mother, prompting her to open the nest and free them.
They remain with her for up to 3 years.
  
|
