Two-toed Amphiuma

| Class: Amphibia:
Amphibians |
Diet: Crustaceans |
| Order:
Urodela: Newts and Salamanders |
| Size: 45
cm - 1.2 m (17 3/4 - 4 ft) |
| Family: Amphiumidae:
Amphiumas |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Amphiuma means |
Habitat: swamps,
bayous, drainage ditches |
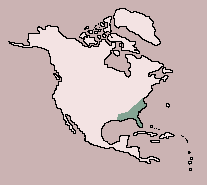
| Range:
USA: Southeastern Virginia to Florida, Eastern Louisiana |
 This
aquatic salamander has tiny, virtually useless limbs, each with two toes.
Mainly active at night, it hunts in water for crayfish, frogs, small snakes
and fish and may come onto land in extremely wet weather. It takes refuge
during the day in a burrow it digs in the mud or takes over the burrow
of another creature. Two-toed amphiumas mate in water, and the female
lays about 200 eggs in a beadlike string. The female coils around the eggs
as they lie on the bottom and protects them until they hatch about 5 months
after being laid. When the larvae hatch, they are about 5 cm (2 in) long;
their tiny limbs are of more use to them at this stage than when they metamorphose
to adult form, at about 7.5 cm (3 in) long. The three-toed amphiuma, Amphiuma
tridactylum, also found in the southern USA, is similar in appearance and
habits but has three toes on each of its tiny limbs. This
aquatic salamander has tiny, virtually useless limbs, each with two toes.
Mainly active at night, it hunts in water for crayfish, frogs, small snakes
and fish and may come onto land in extremely wet weather. It takes refuge
during the day in a burrow it digs in the mud or takes over the burrow
of another creature. Two-toed amphiumas mate in water, and the female
lays about 200 eggs in a beadlike string. The female coils around the eggs
as they lie on the bottom and protects them until they hatch about 5 months
after being laid. When the larvae hatch, they are about 5 cm (2 in) long;
their tiny limbs are of more use to them at this stage than when they metamorphose
to adult form, at about 7.5 cm (3 in) long. The three-toed amphiuma, Amphiuma
tridactylum, also found in the southern USA, is similar in appearance and
habits but has three toes on each of its tiny limbs.
  
|
