Herring Gull

| Class: Aves: Birds |
Diet: Fish, eggs,
waste, young birds, small mammals |
| Order:
Charadriiformes: Auks, Waders, Laris |
| Size: 55
- 66 cm (21 1/2 - 26 in) |
| Family: Laridae:
Gulls, Terns |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Larus argentatus |
Habitat: coasts,
estuaries; inland water and fields |
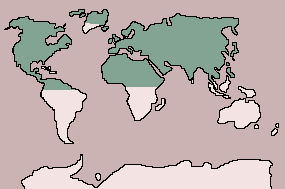
| Range:
Most of Northern hemisphere |
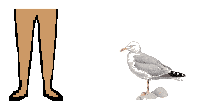 The
commonest coastal gull in North America and Europe, the herring gull feeds
on small surface fish, scavenges on waste and sewage, steals eggs and preys
on young birds and small mammals. It also flies inland to feed on worms
and other invertebrates. Herring gulls nest in colonies on cliff
slopes, islands or beaches. The nest is usually in the ground or is sometimes
built in a tree or even on a building. The 2 or 3 eggs are incubated for
25 to 27 days by both parents. In their first year, the young have dark-brown
plumage, and they do not attain full adult plumage for 3 years. Male and
female adult birds look alike, but males are often larger. The
commonest coastal gull in North America and Europe, the herring gull feeds
on small surface fish, scavenges on waste and sewage, steals eggs and preys
on young birds and small mammals. It also flies inland to feed on worms
and other invertebrates. Herring gulls nest in colonies on cliff
slopes, islands or beaches. The nest is usually in the ground or is sometimes
built in a tree or even on a building. The 2 or 3 eggs are incubated for
25 to 27 days by both parents. In their first year, the young have dark-brown
plumage, and they do not attain full adult plumage for 3 years. Male and
female adult birds look alike, but males are often larger.
  
|
