|
Capybara
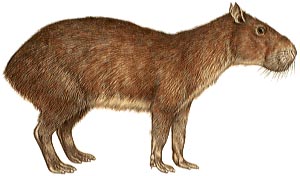
| Class: Mammalia:
Mammals |
Diet: Plants, including
aquatic plants |
| Order:
Rodentia: Rodents |
| Size: body:
1 - 1.3 m (3 1/4 - 4 1/4 ft), tail: vestigial |
| Family: Hydrochoeridae:
Capybara |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris |
Habitat: forest,
near water |
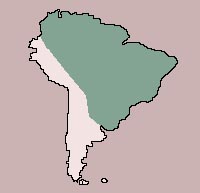
| Range:
Panama to Eastern Argentina |
 The
capybara spends much time in water and is an excellent swimmer and diver;
it has partial webs between the digits of both its hind feet and forefeet.
When swimming, only its eyes, ears, and nostrils show above the water.
Capybaras feed on plant material, including aquatic plants, and their cheek
teeth grow throughout life to counteract the wear and tear of chewing.
They live in family groups and are active at dawn and dusk. In areas where
they are frequently disturbed, capybaras may be nocturnal. Males and females
look alike, but there is a scent gland on the nose that is larger in the
male. They mate in spring, and a litter of 2 young is born after a gestation
of 15 to 18 weeks. The young are well developed at birth.
The
capybara spends much time in water and is an excellent swimmer and diver;
it has partial webs between the digits of both its hind feet and forefeet.
When swimming, only its eyes, ears, and nostrils show above the water.
Capybaras feed on plant material, including aquatic plants, and their cheek
teeth grow throughout life to counteract the wear and tear of chewing.
They live in family groups and are active at dawn and dusk. In areas where
they are frequently disturbed, capybaras may be nocturnal. Males and females
look alike, but there is a scent gland on the nose that is larger in the
male. They mate in spring, and a litter of 2 young is born after a gestation
of 15 to 18 weeks. The young are well developed at birth.
  
|

