Lynx

| Class: Mammalia:
Mammals |
Diet: small-medium
mammals, ground-dwelling birds |
| Order:
Carnivora: Carnivores |
| Size: body:
80 cm - 1.3 m (31 1/2 in - 4 1/4 ft), tail: 4 - 8 cm (1 1/2 - 3 in) |
| Family: Felidae:
Cats |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Felis lynx |
Habitat: coniferous
forest, scrub |
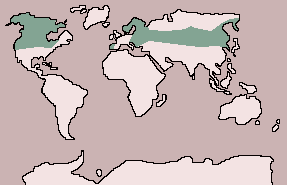
| Range:
Europe: Scandinavia to Spain and Portugal, east through Asia to Siberia;
Alaska, Canada, Northern USA |
 The
lynx is recognized by its short tail and its tufted ears and cheeks. Its
coat varies in coloration over its wide range, particularly in the degree
of spotting, which may be faint or conspicuous. Although strictly protected
in most countries, lynx are becoming scarce, and some races are in danger
of extinction. A solitary, nocturnal animal, the lynx stalks its prey on
the ground or lies in wait for it in low vegetation. Hares, rodents, young
deer and ground-living birds, such as grouse, are its main prey.
Breeding normally starts in the spring, and a litter of 2 or 3 young is
born in a den among rocks or in a hollow tree after a gestation of about
63 days. The cubs remain with their mother throughout their first winter. The
lynx is recognized by its short tail and its tufted ears and cheeks. Its
coat varies in coloration over its wide range, particularly in the degree
of spotting, which may be faint or conspicuous. Although strictly protected
in most countries, lynx are becoming scarce, and some races are in danger
of extinction. A solitary, nocturnal animal, the lynx stalks its prey on
the ground or lies in wait for it in low vegetation. Hares, rodents, young
deer and ground-living birds, such as grouse, are its main prey.
Breeding normally starts in the spring, and a litter of 2 or 3 young is
born in a den among rocks or in a hollow tree after a gestation of about
63 days. The cubs remain with their mother throughout their first winter.
  
|
