Moose

| Class: Mammalia:
Mammals |
Diet: Plants |
| Order:
Artiodactyla: Even-toed Ungulates |
| Size: body:
2.5 - 3 m (8 1/4 - 9 3/4 ft), tail: 5 - 7.5 cm (2 - 3 in) |
| Family: Cervidae:
Deer |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Alces alces |
Habitat: coniferous
forest, often near lakes and rivers |
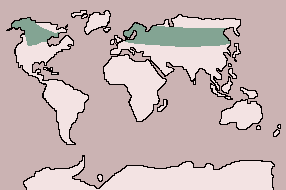
| Range:
Northern Europe and Asia: Scandinavia to Siberia; Alaska, Canada, Northern
U.S.A.; introduced in New Zealand |
 The
largest of the deer, the moose is identified by its size, its broad, overhanging
muzzle and the flap of skin, known as the bell, hanging from its throat.
The massive antlers of the male are flattened and palmate, with numerous
small branches. The moose is less gregarious than other deer and is usually
alone outside the breeding season. In winter, it feeds on woody plants,
but in summer, water plants provide the bulk of its food. It wades
into water to feed and swims well. Following an 8-month gestation, the
female gives birth to a single calf, very rarely to twins. The calf is
suckled for about 6 months but stays with its mother for a year. The
largest of the deer, the moose is identified by its size, its broad, overhanging
muzzle and the flap of skin, known as the bell, hanging from its throat.
The massive antlers of the male are flattened and palmate, with numerous
small branches. The moose is less gregarious than other deer and is usually
alone outside the breeding season. In winter, it feeds on woody plants,
but in summer, water plants provide the bulk of its food. It wades
into water to feed and swims well. Following an 8-month gestation, the
female gives birth to a single calf, very rarely to twins. The calf is
suckled for about 6 months but stays with its mother for a year.
  
|
