Raccoon

| Class: Mammalia:
Mammals |
Diet: Aquatic animals,
rodents, eggs, birds, nuts, seeds, fruit, and corn |
| Order:
Carnivora: Carnivores |
| Size: body:41
- 60 cm (16 - 23 1/2 in), tail: 20 - 40 cm (7 3/4 - 15 3/4 in) |
| Family: Procyonidae:
Raccoons |
Conservation Status:
Non-threatened |
| Scientific Name:
Procyon lotor |
Habitat: wooded areas,
often near water, swamps |
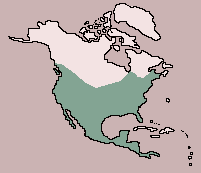
| Range:
Southern Canada, U.S.A., south to Panama |
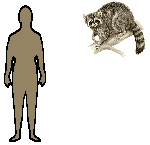 Familiar,
adaptable mammals, raccoons have coped well with the twentieth century
and today are even spotted in cities, scavenging for food. The raccoon
is stocky but agile, with thick, grayish fur and a bushy tail ringed with
black bands; its pointed face has a characteristic "bandit" mask across
the eyes. On the forepaws are long, sensitive digits, which the raccoon
uses with great dexterity when handling food. Mainly active at night, the
raccoon is a good climber and can swim if necessary. Its wide-ranging diet
includes aquatic animals such as frogs and fish, small land animals, such
as rodents, birds, turtle eggs, nuts, seeds, fruit and corn. A litter of
3 to 6 young is born in spring after a gestation of about 65 days. The
young raccoons' eyes are open at about 3 weeks old; they start to go out
with their mother at about 2 months old, remaining with her until autumn. Familiar,
adaptable mammals, raccoons have coped well with the twentieth century
and today are even spotted in cities, scavenging for food. The raccoon
is stocky but agile, with thick, grayish fur and a bushy tail ringed with
black bands; its pointed face has a characteristic "bandit" mask across
the eyes. On the forepaws are long, sensitive digits, which the raccoon
uses with great dexterity when handling food. Mainly active at night, the
raccoon is a good climber and can swim if necessary. Its wide-ranging diet
includes aquatic animals such as frogs and fish, small land animals, such
as rodents, birds, turtle eggs, nuts, seeds, fruit and corn. A litter of
3 to 6 young is born in spring after a gestation of about 65 days. The
young raccoons' eyes are open at about 3 weeks old; they start to go out
with their mother at about 2 months old, remaining with her until autumn.
  
|
